The role of the nurse in patients with coronary artery disease
Sažetak
Uvod: Koronarna bolest danas u razvijenim zemljama je jedan od najvećih uzroka smrti. Koronarna arterijska bolest je sužavanje koronarnih arterija uzrokovana arteriosklerozom, a proizlazi iz akumulacije masnih naslaga, plakova formiranih na unutrašnjoj površini zida koronarnih arterija. Taloženje masnih supstanci dovodi do sužavanja arterija i stenoza, što dovodi do smanjenog snadbijevanja srčanog mišića krvlju i kiseonikom. Tromb, također može dovesti do smanjenja u lumenu ili potpune okluzije (potpuno zatvaranje koronarnih arterija). Kada se radi o kompletnoj stenozi koronarnih arterija dovodi 100% od ishemije miokarda. Koronarna bolest može uzrokovati: akutni infarkt miokarda (sa ST elevacijom i bez-ST elevacijom), anginu pektoris (stabilna, nestabilna, vazospastična), akutni koronarni sindrom, hroničnu ishemijsku bolest srca, iznenadnu srčanu smrt, ishemiju miokarda bez simptoma.
Cilj rada: Ispitati liječenje bolesnika sa STEMI – hospitalizacija u jedinicama intenzivne njege gdje je EIN uz kontinuirano praćenje EKG, krvni pritisak, puls oksimetriju, i invazivne mjerenje centralnog venskog i arterijskog tlaka. Terapijski tretman sa anksiolitikom i analgetskom terapijom (morfin, diazepam), trombolitička terapija (fibrinolize, stent ili bypass), anti-trombocitna terapija, antikoagulansi (heparin), anti-ishemijska terapija (beta-blokatori, ACE inhibitori, nitrati, statini).
Materijali i medtode: Da bi se postigao ovaj cilj, korišteni se deskriptivni i statistički podaci iz Državnog zavoda za statistiku-Skopje i Klinici za kardiologiju – Skopje. Prikazani i sistematizirani napravljeni su razgovori, i na dobijenih informacijama izvučeni su zaključci.
Rezultati: Bolesti srca i krvnih sudova su u stalnom rastu. Smrtnost pacijenata kardiovaskularnih bolesti u Makedoniji je 55-58%.
Diskusija: Broj umrlih od bolesti krvotoka 1975. godine bio je kod 4.714 osoba. Dvadeset godina kasnije, broj slučajeva i smrtnih slučajeva gotovo udvostručio. U 1996- 8878 ljudi umrlo od bolesti srca. U 2003. godini taj broj je porastao na 10.185 osoba, a u 2005. godini bilo je 10.756 smrtnih slučajeva, dok je 2007. godine registrovano samo 11. 311 smrtnih slučajeva zbog kardiovaskularnih bolesti.
Zaključci: S obzirom na sve veći broj bolesti i smrtnosti posebno KAB treba obratiti posebnu pažnju na ranu prevenciji i eliminaciju faktora rizika za sprečavanje pojave KAB. Preventivne mjere treba sprovesti kod porodičnih ljekara i kardiologa kroz edukaciju, organizaciju i provedbu preventivnih mjera. Dugoročni ciljevi zaštite ne samo da se utiču na smanjenje mortaliteta i morbiditeta, nego i na poboljšanje kvaliteta života i smanjenje troškova i opterećenja sistema sekundarne zdravstvene zaštite.
Ključne riječi: koronarna bolest,koronarna arterijska bolest, STEMI.
Summary
Introduction: Coronary disease today in developed countries is one of the biggest causes death.Coronary artery disease is a narrowing of the coronary arteries due to atherosclerosis, resulting from the accumulation of fatty deposits, plaques formed on the inner surface of the wall of the coronary arteries. The deposition of fatty substances leads to narrowing of arteries and stenosis, resulting in reduced supply the heart muscle with blood and oxygen. Thrombus can also lead to a reduction in, or complete occlusion of the lumen (complete closure of the coronary arteries). When we complete coronary artery stenosis occurs 100% of myocardial ischemia. Coronary heart disease can cause acute myocardial infarction (with ST elevation and no-ST elevation), angina (stable, unstable, vasospastic), acute coronary syndrome, chronic ischemic heart disease, sudden cardiac death, myocardial ischemia without symptoms.
Aim: The treatment of patients with STEMI – hospitalization in intensive care units where the EIN with continuous monitoring of ECG, blood pressure, pulse oximetry, and invasive measurement of central venous and arterial pressure. The treatment with an anxiolytic and analgesic therapy (morphine, diazepam), thrombolytic therapy (fibrinolysis, stent or bypass), anti-platelet therapy, anticoagulants (heparin), an anti-ischemic therapy (beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, nitrates, statins).
Materials and methods: In order to achieve this goal, used the descriptive and statistical data from the State Statistical Office Skopje and the Clinic for Cardiology – Skopje. Presented and systematized made the talks, and the obtained information drawn conclusions.
Results: The heart and blood vessels are growing steadily. The mortality rate of patients of cardiovascular disease in Macedonia is 55-58%.
Discussion: The number of deaths from circulatory diseases in 1975 was 4,714 people. Twenty years later, the number of cases and deaths has almost doubled. In 1996- 8878 people died of heart disease. In 2003, that number grew to 10,185 people in 2005, there were 10,756 deaths, and in 2007 he registered only 11 311 deaths due to cardiovascular disease.
Conclusion: In view of the increasing number of diseases and mortality especially CAD should pay particular attention to early prevention and elimination of risk factors to prevent the occurrence of CAD. Preventive measures should be implemented stem physicians and cardiologists through education, organization and implementation of preventive measures. Long-term goals of protection, not only to reduce the mortality and morbidity, but also to improve the quality of life and reduce the cost and burden the system of secondary health care.
Key words: coronary heart disease, coronary artery disease, STEMI.
Introduction
CHD nowadays in developed countries is one of the biggest cause of death. Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a narrowing of the coronary arteries caused by atherosclerosis, which results from the accumulation of fatty deposits, plaques formed on the inner surface of the wall of the coronary artery. Deposition of fatty substances leads to narrowing of the arteries etc. stenosis, resulting in reduced supply the heart muscle with blood and oxygen. Thrombus can also lead to reduction of lumen or complete occlusion (complete closing coronary artery). Commonly occurs in atheromatous plaque rupture and release of thrombus rich in platelets occurs their aggregation and the occurrence of thrombosis. Then it come to a critical stenosis, reducing the lumen of the coronary arteries to 75-99% when exhaust all possibilities for compensation of heart circulation. When we have complete stenosis coronary artery 100% occurs myocardial ischemia.
Aim
The treatment of patients with STEMI – hospitalization in intensive care units where the EIN with continuous monitoring of ECG, blood pressure, pulse oximetry, and invasive measurement of central venous and arterial pressure. The treatment with an anxiolytic and analgesic therapy (morphine, diazepam), thrombolytic therapy (fibrinolysis, stent or bypass), anti-platelet therapy, anticoagulants (heparin), an anti-ischemic therapy (beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, nitrates, statins).
Materials and methods
To achieve this goal preview available primary, secondary and tertiary literature, used data from the State Statistical Office and the Clinic for Cardiology – Skopje. All data was systematized and discussed, and on the information extracted conclusions.
The role of the nurse in patients with coronary artery disease CAD
CAD nowadays in developed countries is one of the biggest cause of death. Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a narrowing of the coronary arteries caused by atherosclerosis, which results from the accumulation of fatty deposits, plaques formed on the inner surface of the wall of the coronary artery. Deposition of fatty substances leads to narrowing of the arteries etc. stenosis, resulting in reduced supply the heart muscle with blood and oxygen. Thrombus can also lead to reduction of lumen or complete occlusion (complete closing coronary artery). Commonly occurs in atheromatous plaque rupture and release of thrombus rich in platelets occurs their aggregation and the occurrence of thrombosis. Then it come to a critical stenosis, reducing the lumen of the coronary arteries to 75-99% when exhaust all possibilities for compensation of heart circulation. When we have complete stenosis coronary artery 100% occurs myocardial ischemia. Coronary artery disease can lead to:
- Acute myocardial infarction
-With ST-segment elevation
-No ST-segment elevation
- Angina pectoris
-Stable
-Unstable (new AP, in peece, worsening)
-Vazospastic
- Acute coronary syndrome
- Chronic ischemic disease
- Suddenly cardiac death
- Asymptomatic myocardial ischemia
Risk factors that lead to CAB include: elevated cholesterol, obesity, decreased physical activity, high blood pressure, smokers, people with diabetes and people who have a genetic predisposition (in family cases with coronary disease).
Symptoms
The most common symptom of CAD is chest pain that occurs in the middle of the chest and spread left hand, rarely in the right arm, jaw, neck, back, and epigastrium. The pain is usually dull, in the form of pressure, tightness, can occur in the form of severe burning or intense pain. The pain is often accompanied by sense of fear, perspiring. Symptoms occur during exertion, stress, excitement and usually spend with the termination of physical exertion, the patient will be calm. The duration of the pain is very important. Anginal pain does not last longer than 5-10 minutes and stops when the patient calm down or will take nitroglycerin pillule. If the pain lasts longer than 20 minutes it is possible to work for myocardial infarction. Stable angina pectoris – is characterized by the occurrence of angina symptoms caused by physical exertion, stress and the cold weather. Symptoms occur only in certain physical effort, with less effort weren’t showed. Acute coronary syndrome – comprising unstable angina and acute myocardial infarction. Anginal pain resulting from very small physical effort and limit the strain from which the symptoms occur are narrowing. Unstable angina can occur from stable or to appear as a new disease in previously healthy patient. Myocardial infarction – can be divided into infarction without ST- elevation myocardial sementot and with and without Q-venomouse.
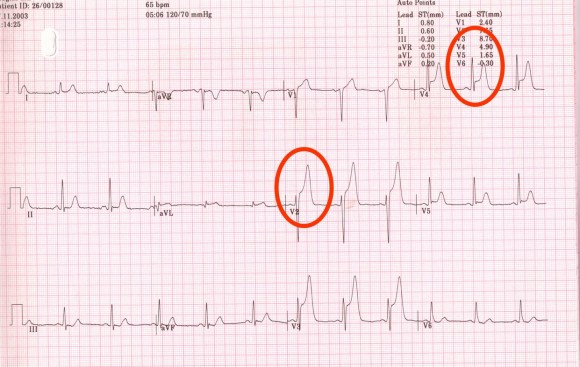
Picture 1. ST- elevation myocardial sementot and with and without Q-venomouse
Sudden cardiac death – is the unexpected death from cardiac causes within one hour of the initial complaint to the moment of death. Often caused by heart arrhythmias arising from coronary disease.Chronic ischemic disease – is caused by a decrease in heart function and heart will pump power to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body.
Asymptomatic coronary disease – is most common in patients with diabetes and smokers because among them may occur damage to the nerve pathways that transmit pain.
Diagnostic methods
Physical examination, electrocardiogram (ECG), laboratory tests (lipid status, troponin, CK-MB, myoglobin, blood glucose, blood …), coronary stress test CPT, Doppler echocardiography, myocardial perfusion scintigraphy, Doppler of carotid arteries coronary angiography, computerized tomography CT, magnetic resonance imaging of the heart.
Treatment of patients with STEMI – hospital treatment EIKN where under continuous ECG monitoring, blood pressure, pulse oximetry and invasive measurement of central venous and arterial pressure. Therapeutic treatment with anxiolytic and painless therapy (morphine, diazepam), reperfusion therapy (fibrinolysis, stent or bypass), anti-trobocitna therapy (ASA), anticoagulants (heparin), anti-ischemic therapy (beta-blockers,AKEinhibitori,nitrates, statins). Treating complications: mechanical (defects, rupture, aneurysm surgery), disturbance of electrolytes – correction.
First contact with the patient’s nurse briefly taken nursing history. The role of the nurse is to constantly monitor the patient from admission to its release noting any changes that inform the doctor. The nurse explains to patients about their disease with simpler language so they can understand the nature of their disease as they could and the patients themselves to cooperate to take the recommended therapy, conduct hygiene dietary regime and thereby contribute to their fast recovery.
Results and discussions
The heart and blood vessels are growing steadily. The mortality rate of patients of cardiovascular disease in Macedonia is 55-58%.
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels are in constant growth. Mortality of patients of cardiovascular disease in Macedonia is 55-58%. The number of deaths from diseases of the circulatory system in 1975 was 4,714 persons. Twenty years later, the number of cases and deaths almost doubled. In 1996 8878 people died of heart disease. In 2003 this number increased to 10,185 persons in 2005 there were 10,756 deaths, and in 2007 were registered only 11 311 deaths due to cardiovascular disease. All this shows that the number of cases is increasing rapidly. Doctors agree that more and more people suffer from heart disease, but say that the number of cases yet to growing.According data of the State Statistical Office in 2012 from diseases of the circulatory system killed 11 926 persons, of which 5739 were men and 6187 were women with total mortality rate of 578 per 100,000 inhabitants. A significant cause of death in the structure of circulatory diseases with 100 deaths per 100,000 or about 2,000 deaths annually participate ischemic heart disease. Every year they register more than 3,000 heart-disease parks.
Chart number 1.
Because early diagnosis of CAD and better prognosis doing coronary angiography. In 2012 they were made coronarographies 5132, 2013 coronarographies 6177 and 2014 6461 coronarographies.
Chart number 2. Total coronary angiography
Of elective coronary angiography in 2012 of these were 377 patients stenting and 251 were referred for bypass, and the rest were for conservative treatment. In 2013 stenting were 591 patients, 178 were referred for bypass surgery and the rest were treated conservatively. In 2014 the total number of 273 patients were elective stenting, 180 were referred for bypass surgery and the rest were treated conservativey.
Chart number 3.
Сonclusion
Given the growing number of disease and mortality especially CAD should pay special attention to early prevention and elimination of risk factors to prevent the occurrence of CAD. Preventive measures should be implemented by the primary care physician and cardiologists through education, organization and implementation of preventive measures. Term goals of care not only to reduce mortality and morbidity, but also to improve the quality of life and reduce the cost and burden of secondary health care systems. Special care improves if provided by a specialized team and with a multidisciplinary approach. Sisterhood play a greater role in the care of this condition, not only providing care during acute episodes of illness requiring hospitalization, but also in providing the health promotion and education, handing out flyers and brochures to familiarize patients with their condition and acceptance of drug therapy.
Reference
1.Cardiac nursing – Richard Hatchett; David R. Thompson
2.Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine – Dr.Anthony S. Fauci; dr.Denis L. Kasper; Dr. Dan L. Long; Dr. Jugin Braunvald; Dr. S.L.Hauzer; Pprof.dr. G.Lary Gejmison; Prof.dr.Joseph Loskalco.
3.Coronary arterial disease prevention, diagnosis, treatment – Ljubica Georgievska-Ismail
4.Therapeutic guide for doctors, pharmacists and dentists 2006 year. – Prof.dr. Borche Petrovski; Prof.dr. Silvana Jovanova; Prof.dr. Samuel Sadikario; Prof.dr. Lidija Petrushevska- Tozi; Doc.dr. Renata Slavevski Raicki.
5.Нега на болен- проф.Д-р Гордана Панова
6.Одбрани поглавја од интерна медицина – доц.Д-р Марија Вавлукис, асс. Д-р гордана Камчева, асс.Д-р Валентина Велковска Накова, асс.Д-р Анѓела Добрешлиоска.
7.Анестезиологија со реанимација-М. Шољакова и други автори
8.Lipincot Manual for nurses